MMD Camera
This section describes the MmdCamera class and the IMmdCamera interface, which reproduce the camera behavior of MMD.
MmdCamera class
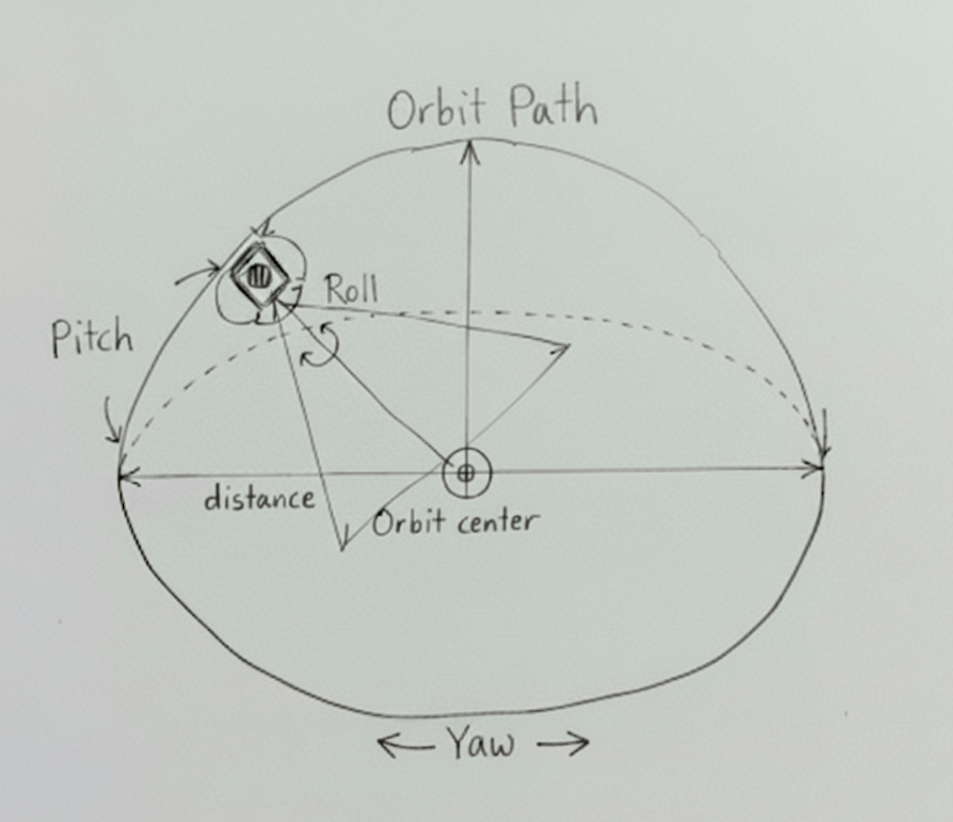 Visual representation of the MMD camera orbit path
Visual representation of the MMD camera orbit path
The camera in MMD is an Orbit Camera that rotates around a center position.
The MmdCamera class reproduces this, and therefore the parameters for controlling the camera are as follows:
- position (Vector3) - Orbit center position
- rotation (Vector3) - Yaw Pitch Roll
- distance (number) - Distance from the Orbit center
- fov (number) - Field of view in radians
The MmdCamera class inherits from Babylon.js Camera class. Therefore, like other Babylon.js cameras, it can be added to the Scene for use.
Creating a Camera
You can create an MmdCamera and add it to the Scene with the following code:
const mmdCamera = new MmdCamera("mmdCamera", new Vector3(0, 10, 0), scene, true);
Each parameter means the following in order:
- name: Camera name
- position: Initial Orbit center value (default: (0, 10, 0))
- scene: Scene to add the camera to (default: Engine.LastCreatedScene)
- setActiveOnSceneIfNoneActive: Whether to set this camera as the active camera in the Scene if no other camera is defined after creation (default: true)
Animation Binding
The MmdCamera can bind and use MmdAnimation created from VMD or BVMD files.
const vmdLoader = new VmdLoader();
const mmdAnimation = await vmdLoader.loadAsync("path/to/file.vmd");
const mmdCamera = new MmdCamera("camera", new Vector3(0, 10, 0), scene);
const animationHandle: MmdRuntimeAnimationHandle = mmdCamera.createRuntimeAnimation(mmdAnimation);
The code above is an example of loading a VMD file to create an MmdAnimation and binding it to an MmdCamera.
You can create a bound "Runtime Animation" using the MmdCamera.createRuntimeAnimation method. The result returned by the function is not the actual runtime animation object but a handle to the object.
runtimeAnimations
The created runtime animation object is added to MmdCamera.runtimeAnimations.
This allows for more low-level control by accessing the actual runtime animation object rather than the proxy.
Using Animation
To use the bound runtime animation, call the MmdCamera.setRuntimeAnimation method:
mmdCamera.setRuntimeAnimation(animationHandle);
By default, the MmdCamera object can only play one animation at a time.
To remove the currently set animation, pass null as an argument:
mmdCamera.setRuntimeAnimation(null);
The currently set animation can be accessed through the MmdCamera.currentAnimation property.
Destroying Runtime Animation
To destroy a runtime animation bound to the MmdCamera, call the destroyRuntimeAnimation method:
mmdCamera.destroyRuntimeAnimation(animationHandle);
If you don't destroy camera runtime animations that are no longer used, memory leaks won't occur, but runtime errors might occur in some special cases.
Evaluating Animation
You can evaluate the currently set animation using the MmdCamera.animate() method.
This method is typically not called directly but is called by the MMD runtime.
If you are manually controlling the MmdCamera, you can call this method to evaluate the animation:
let sec = 0;
scene.onBeforeRenderObservable.add(() => {
const frameTime = sec * 30; // MMD operates at 30fps
mmdCamera.animate(frameTime); // Evaluate animation. Pass time scaled in 30 frame units as a parameter
sec += engine.getDeltaTime() / 1000;
});
IMmdCamera interface
babylon-mmd provides the IMmdCamera interface to allow users to implement their own MMD camera.
All components of babylon-mmd use the IMmdCamera interface instead of the MmdCamera class type to reference or pass MMD camera objects.