Use Babylon.js Animation Runtime
Using Babylon.js's animation system to play MMD animations offers the following advantages:
- Babylon.js Animation Curve Editor support
- Animation Blending support
- More generalized animation management
Therefore, babylon-mmd provides methods to play MMD animations using Babylon.js's animation system.
Babylon.js Animation System Architecture
First, it's necessary to understand the capabilities of Babylon.js's animation system architecture.
Babylon.js Animation
In Babylon.js, animations are primarily represented using Animation objects.
An Animation object is a container that stores animation keyframes for a specific property.
There are 8 types that can be controlled by animations:
Float(number)Vector3QuaternionMatrixColor3Color4Vector2Size
Each type uses different interpolation methods.
For example, the Float type uses linear interpolation, while the Quaternion type uses spherical linear interpolation (SLERP).
The Animation object provides an _interpolate method that evaluates values for time t.
However, it does not include the logic for applying animations to binding targets.
Babylon.js Runtime Animation
RuntimeAnimation is responsible for actually evaluating Animation objects and binding them to targets.
Part of the animation's evaluation logic and the logic for binding path resolution are implemented in the RuntimeAnimation object.
Babylon.js Animatable
Animatable is responsible for managing multiple RuntimeAnimation objects and updating animations in sync with the Scene's rendering loop.
Complex animation blending logic is also handled here. (Babylon.js supports animation blending.)
Therefore, we can use Animatable objects to simultaneously play multiple RuntimeAnimation objects to play MMD model animations as follows:
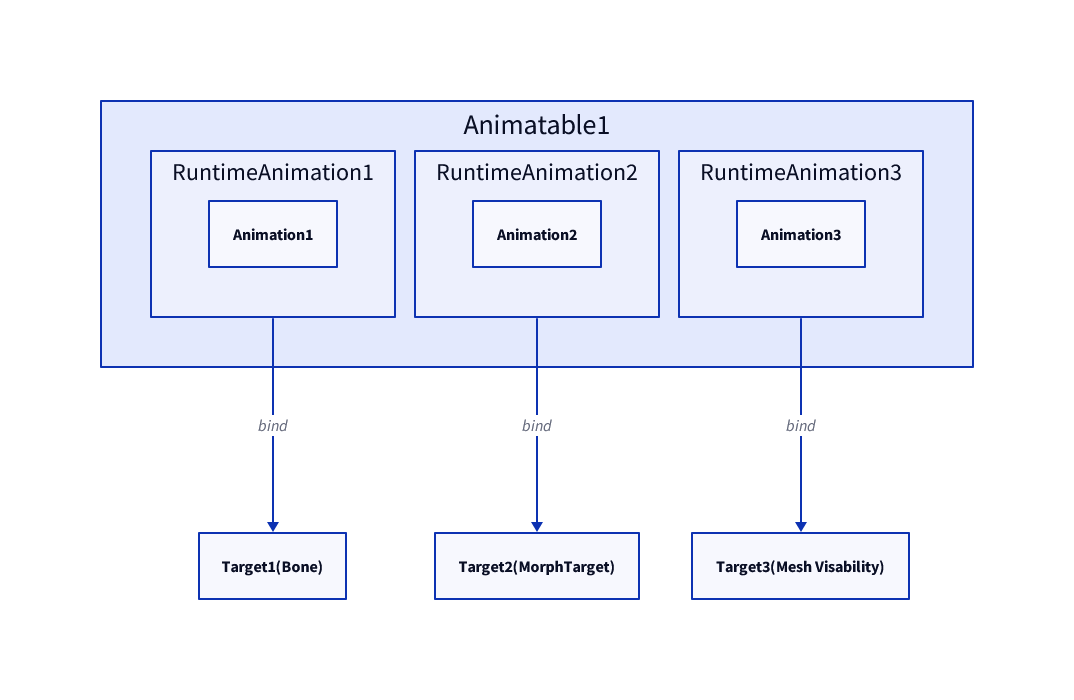 This diagram shows the reference relationships between
This diagram shows the reference relationships between Animatable, RuntimeAnimation, Animation objects and binding targets.
Since babylon-mmd does not directly use the Animatable object approach, the actual diagram is somewhat different.
Babylon.js Animation Group
AnimationGroup is a container that manages Animation objects and binding targets as pairs.
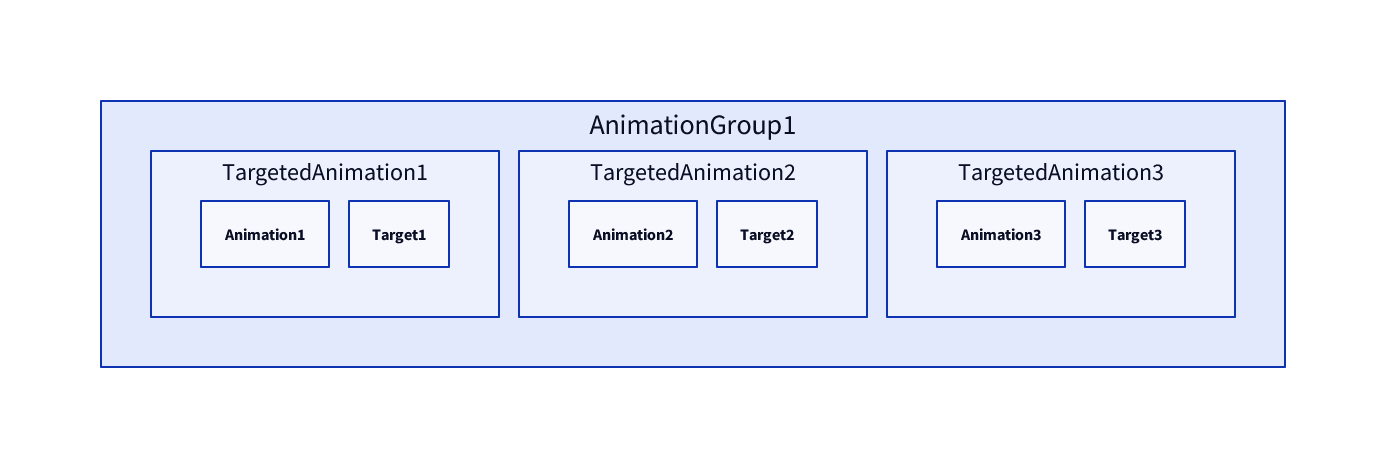 This diagram shows how
This diagram shows how AnimationGroup manages Animation objects and binding targets as pairs.
AnimationGroup internally uses Animatable objects to play animations. It provides a higher-level API to make it easier to use.
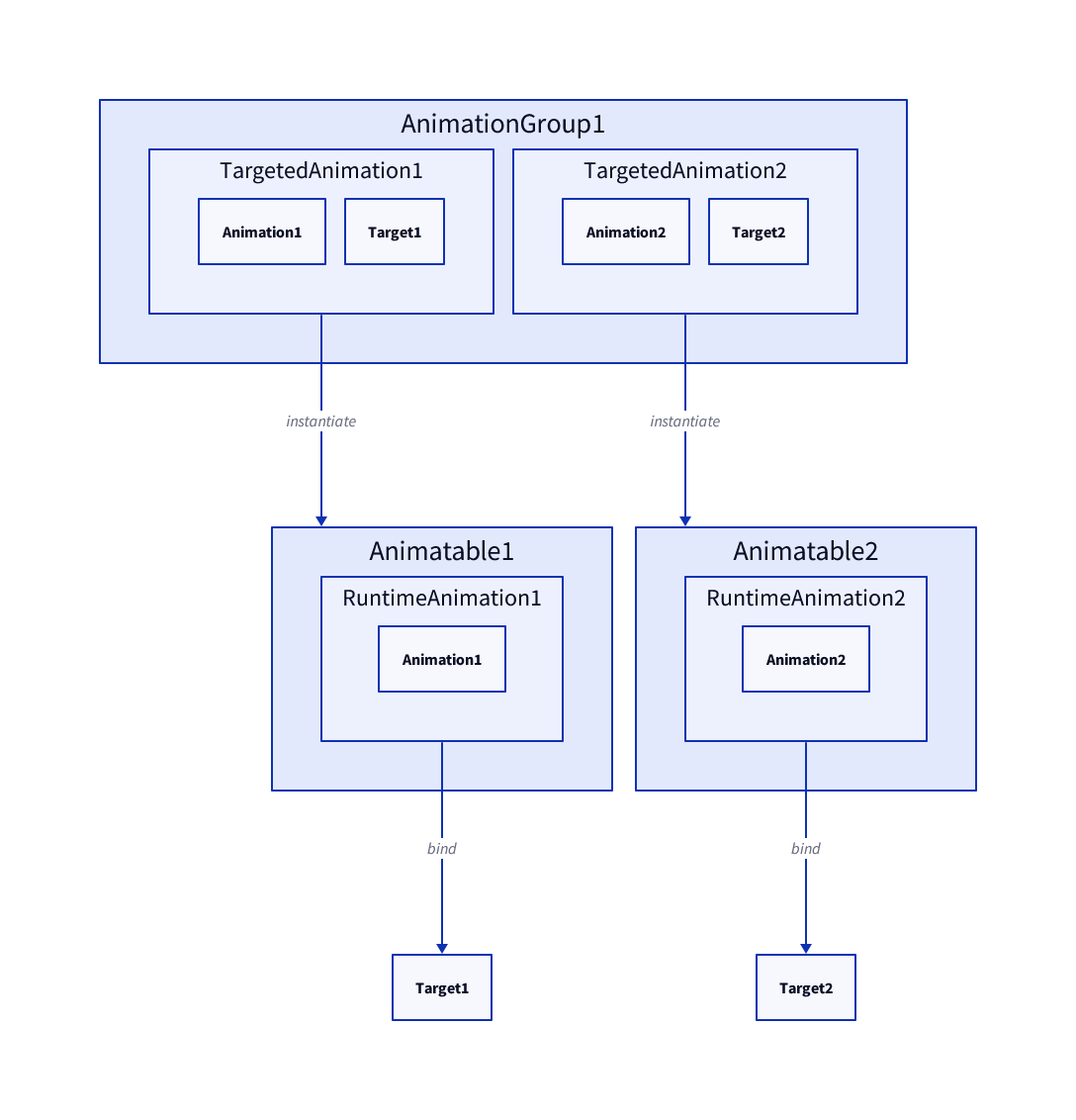 This diagram shows how
This diagram shows how AnimationGroup internally uses Animatable objects to play animations.
Using Babylon.js Animation System to Play MMD Animations
There are two main methods provided for using Babylon.js's animation system to play MMD animations:
- Direct binding after animation evaluation using the
Animationobject's_interpolatemethod - Using
AnimationGroupobjects for animation evaluation and binding
The advantages and disadvantages of each method are as follows:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Method 1 (Using Animation) | Babylon.js Animation Curve Editor support | Performance degradation and increased memory usage compared to MmdAnimation |
| Method 2 (Using AnimationGroup) | All features of Babylon.js Animation System available | Greater performance degradation and more memory usage compared to Method 1 |
Now let's explore how to use these two methods to play MMD animations.
The Animation Container Class
An Animation object is a container that stores animation keyframes for a single property.
However, the MMD animations we handle contain animation keyframes for multiple properties.
Therefore, babylon-mmd provides container classes MmdCameraAnimationContainer and MmdModelAnimationContainer that manage multiple Animation objects together.
MmdCameraAnimationContainer and MmdModelAnimationContainer manage collections of Animation objects designed to be applied to MmdCamera and MmdModel respectively.
They are created as follows:
const modelBezierBuilder = new MmdModelAnimationContainerBezierBuilder();
const cameraBezierBuilder = new MmdCameraAnimationContainerBezierBuilder();
const mmdModelAnimationContainer = new MmdModelAnimationContainer(mmdAnimation, modelBezierBuilder);
const mmdCameraAnimationContainer = new MmdCameraAnimationContainer(mmdAnimation, cameraBezierBuilder);
Note that when creating animation containers, a builder is passed along.
This is because Babylon.js's animation system does not fully support MMD animation's interpolation methods.
Babylon.js does not support Bézier interpolation between keyframes, and the three main interpolation methods provided by default are:
- Linear
- Step
- Hermite
Hermite interpolation implements Cubic Spline interpolation using inTangent and outTangent, which has lower degrees of freedom than Bézier interpolation.
Therefore, babylon-mmd provides three options to support Bézier interpolation:
Mmd(Model/Camera)AnimationContainerHermiteBuilder: CreatesMmd(Model/Camera)AnimationContainerusing Hermite interpolation.- This method approximates Bézier interpolation tangents to Hermite interpolation tangents. This method has lower accuracy and may show significant differences, especially in camera animations.
Mmd(Model/Camera)AnimationContainerSampleBuilder: Approximates Bézier interpolation with linear interpolation.- This method samples Bézier curves at 30-frame intervals and approximates them with linear interpolation. This method has high accuracy but increases memory usage. It also has the disadvantage that animations become non-editable.
Mmd(Model/Camera)lAnimationContainerBezierBuilder: Accurately implements Bézier interpolation.- This method accurately implements Bézier interpolation by overriding the
Animationobject's_interpolatemethod. This is the most accurate method, but since it forcibly adds non-existent interpolation methods by overriding theAnimationobject's_interpolatemethod, tools like Animation Curve Editor may not work properly.
- This method accurately implements Bézier interpolation by overriding the
The created MmdModelAnimationContainer and MmdCameraAnimationContainer can be bound to MmdModel and MmdCamera respectively. Depending on the binding method, it determines whether to use only the Animation object's _interpolate method or to use RuntimeAnimation and Animatable objects through AnimationGroup.
Method 1: Using Animation Object
babylon-mmd provides runtime implementations that directly bind MmdModelAnimationContainer and MmdCameraAnimationContainer.
This can be used by importing the "babylon-mmd/esm//Runtime/Animation/mmdRuntimeCameraAnimationContainer" and "babylon-mmd/esm/Runtime/Animation/mmdRuntimeModelAnimationContainer" modules.
import "babylon-mmd/esm/Runtime/Animation/mmdRuntimeCameraAnimationContainer";
import "babylon-mmd/esm/Runtime/Animation/mmdRuntimeModelAnimationContainer";
This allows you to bind Mmd(Camera/Model)AnimationContainer using the createRuntimeAnimation method on MmdCamera and MmdModel objects in the same way as binding MmdAnimation.
const camera: MmdCamera = ...;
const model: MmdModel = ...;
const cameraAnimationHandle = camera.createRuntimeAnimation(mmdCameraAnimationContainer);
const modelAnimationHandle = model.createRuntimeAnimation(mmdModelAnimationContainer);
Method 2: Using AnimationGroup Object
MmdModelAnimationContainer and MmdCameraAnimationContainer provide the createAnimationGroup method for creating AnimationGroup objects.
const modelAnimationGroup = mmdModelAnimationContainer.createAnimationGroup("modelAnimation", mmdModel);
const cameraAnimationGroup = mmdCameraAnimationContainer.createAnimationGroup("cameraAnimation", mmdCamera);
Now you can play animations using the AnimationGroup API.
modelAnimationGroup.play(true);
cameraAnimationGroup.play(true);
AnimationGroup objects provide multiple features including not only playback but also blending of multiple animations. For more details, refer to the Babylon.js official documentation.
When using AnimationGroup objects to play animations, the MMD runtime is no longer the execution entity for animations, so even if you add audio to the MMD runtime, audio and animations will not be synchronized.